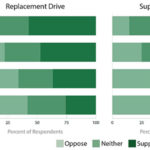
Does the US public support using gene drives to control agricultural pests?
Mike Jones, Sep. 11, 2019 | The development of gene drives is progressing more rapidly than our understanding of public values towards these technologies. Findings from this research can inform responsible innovation in gene drive development and risk assessment....Continue reading "Does the US public support using gene drives to control agricultural pests?"

Workshop Report on Gene Drive Mice for Biodiversity Protection on Islands
S. Kathleen Barnhill-Dilling, June 24, 2019 | Mice offer an ideal genetic model for exploring the possibility of developing a synthetic gene drive in mammals. As pests, they pose challenges to human health, agricultural yields and storage, and biodiversity, especially on islands where they are not native. If research on gene drives in mice were to progress to a field trial, an island ecosystem would offer an additional level of physical containment. ...Continue reading "Workshop Report on Gene Drive Mice for Biodiversity Protection on Islands"

IUCN Report: Genetic frontiers for conservation – An assessment of synthetic biology and biodiversity conservation
Todd Kuiken, May 9, 2019 | Synthetic biology – altering or redesigning genes to meet human objectives – is a fast-developing field with significant potential impacts on nature conservation, according to the Genetic frontiers for conservation assessment report. So far mostly applied in agriculture and medicine, synthetic biology could have substantial knock-on effects on conservation – including modified genes spreading to non-target species and affecting broader ecosystems, but also benefits such as saving threatened species, reduced fertiliser use or diminished demand for products derived from threatened species....
Report: Stakeholder Perspectives on Gene Drive Mice for Biodiversity Protection on Islands
Jason Delborne, February 20, 2019 | This article reviews the current state of gene-editing regulation for crops, illuminating the ways in which technology developers are repeating practices that may lead to the public and ethical failures of the first generation genetically engineered crops, and argues that the contentious socio-political history of genetic engineering will repeat itself for gene editing if these continue....